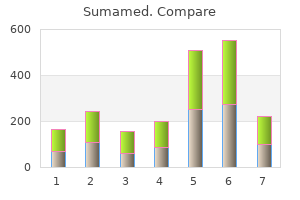
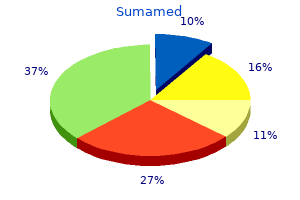
"Order 500 mg sumamed otc, antimicrobial 7287."
By: Pierre Kory, MPA, MD
- Associate Professor of Medicine, Fellowship Program Director, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, Mount Sinai Beth Israel Medical Center Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York

https://www.medicine.wisc.edu/people-search/people/staff/5057/Kory_Pierre
Basilar artery syndromes include the midbrain syndromes antimicrobial keyboard and mouse safe sumamed 250 mg, paramedian thalamic and subthalamic syndromes how much antibiotics for sinus infection sumamed 250mg without a prescription. In this setting antibiotic nomogram buy sumamed 100 mg, many perforator vessels are affected and the presentation is clearly more severe than one of the lacunar syndromes. Occlusion of the entire basilar artery (typically involving the lower third of the artery) is generally thrombotic from build-up of atherosclerotic plaque, and results in the so-called complete basilar syn drome. When perfusion is insufficient to spare the reticular activating, a rare, but devastating syndrome termed locked-in can occur. While brain stem syndromes are not associated with neuropsychological deficits, patients with a Top of the Basilar syndrome exhibit memory impairment. In general, patients suffering brain stem or midbrain infarcts tend to exhibit persistent deficits with poor quality of life. Neuropsychologic deficits Primary visual cortex Visual hallucinations (poorly formed) Dorsomedial thalamic Memory impairment (poor encoding and nuclei (bilateral) consolidation reflecting anterograde Intralaminar thalamic amnesia) nuclei Apathy and abulia. Note: Patient is awake and alert due to sparing of midbrain and reticular formation. Somatosensory pathways (touch, temperature, pain, proprioception, and vibration sense) often intact (intact medial lemniscus). Facial hemiparesis Horizontal gaze palsy Other symptoms: Dysarthria No neuropsychological impairment Medial superior Contralateral: Occlusion of paramedian pontine syndrome Hemiparesis (face, arm, leg) branches of upper Can be hemianesthesia (touch, vibration, basilar artery. Diplopia on lateral gaze Cerebellar ataxia Other symptoms: Dysarthria No neuropsychologic impairment (continued) 13 Cerebrovascular Disease and Stroke 337 Table 13. Sensation of light touch, proprioception of Vertebral and and vibration sense Anterior Spinal arteries Ipsilateral: (paramedian branches) Tongue weakness Infarct of medial medulla No neuropsychological impairment (damaging pyramidal tract, medial lamniscus, and hypoglossal nucleus) Wallenbergs Contralateral: Lesion to lateral medulla syndrome Loss of body sensation (arm and leg) to (damaging the inferior pain and temperature cerebellar peduncle, Ipsilateral: vestibular nuclei, Ataxia (arm and leg) trigeminal nucleus, spinothalamic tract, and Loss of facial sensation to pain and sympathetic fibers) temperature Paralysis of soft palate, pharynx and vocal cord resulting in dysphagia and hoarseness Horners syndrome Other symptoms: Nausea and vertigo often present Nystagmus No neuropsychological impairments 338 C. The differentia diagnosis of vascular dementia with 13 Cerebrovascular Disease and Stroke 339 Image O. Treatment of stroke will likely include acute management of symptoms, rehabilitation and pharmaceutical intervention for medical risk factors. Patients may also be prescribed medications with cognitive side effects, such as anticonvul sants (for seizure prophylaxis), antidepressants, anxiolytics and antipsychotics for concomitant mood and behavioral disorders. Rehabilitation after stroke commonly includes speech and language therapy, cognitive therapy, physical therapy, occupa tional therapy, and vocational therapy. Deficits in neuropsychological function will depend upon size and location of lesion, time elapsed since the stroke, as well as the patients age and co-morbid conditions. Although there is marked variability in the type and severity of neurologic/neurop sychologic comorbidities of cortical and subcortical strokes, recovery following damage to cortical structures and supratentorial white matter is more complete than recovery from deep pathways within the brain stem. While brain stem strokes are often more life threatening given the likelihood of affecting basic life support cen ters, they often produce profound physical impairment but may spare cortical areas and subsequently many cognitive processes (attention/executive, memory, lan guage, vision, reasoning, personality, etc. Cortical strokes in contrast produce the greatest risk for cognitive functioning deficits. When to Conduct a Neuropsychological Evaluation Neuropsychological assessment may be completed any time following a stroke. Common referral questions include requests to document the nature of the deficit, help develop rehabilitation interventions and/or placement decisions, assess for pro gression of neuropsychological functional recovery, and/or identify the development of complicating conditions. Neuropsychological assessment can be particularly helpful for patients with recov ery that is mostly complete (and only subtle deficits are present), but continue to cause problems with work, school, or at home (see Victor and Ropper 2001 and Lezak et al. In the acute and subacute stages, we recommend neu ropsychological assessment be completed using brief bedside methods rather than administration of detailed or lengthy neuropsychological evaluation. Accommodation and adapta tion of neuropsychological tests is often necessary in acute and sub-acute stroke assessments. For example, presenting visual memory material in the right hemispace will better allow for assessment of visual memory function 342 C. Neuropsychological evaluation may also be requested months to years after a stroke, and is particularly helpful in evaluating the extent and severity of residual neu ropsychological deficits, identify strengths to assist with developing accommodation and adaptations along with speech/language and physical therapy (Lezak et al. Additionally, neuropsychological evaluation can also assist in determining the patients competence to manage his/her personal affairs, make medical/legal/financial deci sions, and/or capacity, and accommodations for the ability, to return to employment. In these cases, more detailed psychometric evaluation of the patients neuropsycho logical functioning is often completed.
Identification of these syndromes is paramount to virus news order sumamed 250mg amex providing these children and their families a First described in 1597 (17) virus games effective sumamed 100mg, the specific electrographic and favorable prognosis and appropriate management bacteria definition for kids buy 100mg sumamed mastercard. Rolandic spikes were noted to be unrelated to childhood include (2,3): focal pathology in 1952 (18) and could be observed without clinical seizures (19). Chapter 19: Idiopathic and Benign Partial Epilepsies of Childhood 245 status epilepticus, as well as cognitive and behavioral distur Pathophysiology bances are seen. The number of axonal 10% experience neonatal difficulties (including 3% with branches and synaptic connections is greater early in develop neonatal seizures), 4% to 5% have preceding mild head ment and pruning of these connections may limit the injuries, and up to 16% have antecedent febrile seizures (32). Spikes have a characteristic horizontal dipole, with jaw or tongue and a choking sensation are common. During maximal negativity in centrotemporal (inferior rolandic) and sleep, seizures may secondarily generalize (32). The focus is uni parasthesias or jerking of a single arm or leg, abdominal pain, lateral in 60% of cases, bilateral in 40%, and may be synchro blindness, or vertigo may be seen and likely reflect seizure foci nous or asynchronous (32). Seizures often occur in mum electronegativity at C3/C4 and seizures with frequent clusters, followed by long seizure-free intervals. Atypical spike location is not Postictal Todd paresis occurs in 7% to 16% of cases and uncommon. Follow-up recordings Seizure duration is typically brief, lasting seconds to several showed shifts in foci both toward and away from the cen minutes; however, status epilepticus has been described trotemporal area. Temporary oromotor and speech disturbances with mild slowing has been observed (48). Eventually, all children recover from the waking record and later from the sleep recording over 6 months to 8 years but may be left with mild speech dys (32). Ictal Positron emission tomography demonstrated a bilateral spike-and-wave discharges may show dipole reversal, with increase of glucose metabolism in the opercular regions in one electropositivity in the centrotemporal region and negativity patient with this type of nonconvulsive status (55). In rolandic sharp waves who develop clinically apparent seizures addition to partial motor seizures, frequent atonic, atypical is unclear. Reading disabil ropsychological abnormalities was seen, indicating that they ity and speech sound disorder occur more commonly both in are also benign and resolve around the time of puberty. Younger age at the expected left lateralization of language was seen in all seizure onset also appears predictive of cognitive difficulties. However, a study of academic performance in 20 children with rolandic those with left centrotemporal discharge demonstrated epilepsy, Piccinelli found greater cognitive difficulties in those bihemispheric representation of language, raising the possibil with seizure onset before age 8 years and those with greater ity that focal epileptic activity may alter cerebral mechanisms activation of epileptiform discharge during sleep (89). Prospective studies (80,90,91) have shown that, like the Similarly, in a study of attention and processing of visuo seizures and epileptiform discharges, the cognitive difficulties motor information, a right hemispheric task, in 43 right also appear to resolve with time. Because they appear controls or those with left centrotemporal discharge, suggest to correlate with the amount and side of interictal spike dis ing that focal epileptic discharge in the right hemisphere may charge, these discharges may cause transient cognitive interfere with visuomotor processing (86). Neuropsychological deficits were not related to neurologically and developmentally intact, no further investi presence or absence of seizures, seizure frequency, lateraliza gations are required. A no-medication strategy is reasonable of age-appropriate siblings may help support the diagnosis of for the majority of children who have infrequent, nocturnal, highly atypical cases. If recurrent generalized or diurnal seizures with other central nervous system pathologic findings, yet the occur, or if the seizures are sufficiently disturbing to the child prognosis appears to be as favorable in brain-injured patients or the family, treatment is generally started. Short intervals between the initial seizures and pocampal asymmetries in 28% and white-matter abnormali younger age at onset predict higher seizure frequency. The latter finding may indicate maturational child who presents with status as their first manifestation of delay with defective myelination, but the hippocampal changes rolandic epilepsy, abortive therapy with benzodiazepines is a were unexplained. Sulthiame does decrease interictal discharge, and while Gibbs and Gibbs were the first to recognize that some chil it is tempting to think that it may improve neuropsychological dren with occipital epilepsy had a benign course (108). The peak age of onset is 5 years (range, 2 Seizures may initially appear refractory in a small number of to 8 years) with a female preponderance. Other investigators (112,113) have meta-analysis, 50% of patients were in remission at age 6 years, found that most affected children lack a family history of 92% at age 12 years, and 99. Remission occurs sooner in children older at onset and in occipital epilepsy, including seven twins, Taylor found that those with sporadic seizures or seizure clusters (46). Although monozygotic twin pairs did not show a higher concordance learning and behavior problems may be seen in the acute phase, rate than dizygotic twin pairs, suggesting that this condition long-term psychosocial outcome is excellent (107), with no was not purely a genetic disorder and that nonconventional increase in psychiatric problems or personality problems, and genetic influences or environmental factors play a major excellent occupational status. The course of benign partial epilepsy of childhood with centrotem poral spikes: a meta-analysis.
Sumamed 500 mg mastercard. ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECT OF PLANT EXTRACTS.
Anti oxidant features of red wine pyranoanthocyanins: experimental and theoretical approaches infection z cast cheap sumamed 100 mg with mastercard. Inhibition of amylase and glucoamylase by tannins extracted from cocoa antibiotics quiz pharmacology discount 500 mg sumamed with amex, pomegranates virus neutralization assay effective sumamed 250mg, cranberries, and grapes. Current understanding of lifestyle and environmental factors and risk of non-hodgkin lymphoma: an epidemiological update. Inhibition of aggregation and secretion of human platelets by quercetin and other favonoids: structure-activity relationships. Amyloid beta-protein oligomerization: prenucleation interactions revealed by photo-induced cross-linking of unmodifed proteins. Bioavailability and biokinetics of anthocyanins from red grape juice and red wine. Hypolipidemic effects of proanthocyanidins and their underlying biochemical and molecular mechanisms. In vivo interactions between procyanidins and human saliva proteins: effect of repeated exposures to procyanidins solution. Kinetic and thermody namic study of proton transfer, hydration, and tautomeric reactions of malvidin 3-glucoside. Repeat dose study of the cancer chemopreventive agent resveratrol in healthy volunteers: safety, pharmacokinetics, and effect on the insulin-like growth factor axis. Malvidin-3-glucoside bioavail ability in humans after ingestion of red wine, dealcoholized red wine and red grape juice. Anthocyanins are detected in human plasma after oral administration of an elderberry extract. Effects of alcohol and polyphenols from beer on atherosclerotic biomarkers in high cardiovascular risk men: a randomized feeding trial. The International Journal of Angiology: Offcial Publication of the International College of Angiology, Inc. In vitro fermentation of grape seed favan-3-ol fractions by human faecal microbiota: changes in microbial groups and phenolic metabolites. Human metabolism and elimination of the anthocyanin, cyanidin-3-glucoside: a 13C-tracer study. Urinary biomarkers of oxidative stress and plasmatic infammatory profle in phenylketonuric treated patients. Transport of proanthocyanidin dimer, trimer, and polymer across monolayers of human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Characterization of interactions between polyphenolic compounds and human serum proteins by capillary electrophoresis. Changes in polyphenol profles and color composition of freshly fermented model wine due to pulsed electric feld, enzymes and thermovinifcation pretreatments. A pilot study to investigate if New Zealand men with prostate cancer beneft from a Mediterranean-style diet. Insights into the putative catechin and epicatechin transport across blood brain barrier. Blueberry antho cyanins and pyruvic acid adducts: anticancer properties in breast cancer cell lines. Strawberry pel argonidin glycosides are excreted in urine as intact glycosides and glucuronidated pelargonidin derivatives in rats. Moderate consumption of white and fortifed wine is associated with reduced odds of diabetic retinopathy. Bioavailability of anthocyanidin-3 glucosides following consumption of red wine and red grape juice. Electron spin resonance spectroscopy studies on the free radical scavenging activity of wine anthocyanins and pyranoanthocyanins. Study of the interaction of pancreatic lipase with procyanidins by optical and enzymatic methods. How wine polyphenols can fght Alzheimer disease progression: towards a molecular explanation. Exercise at lunchtime: effect on glycemic control and oxidative stress in middle-aged men with type 2 diabetes. Minimum prices for alcohol and educational dispari ties in alcohol-related mortality.
Reduction of the viscosity of fermented cereal-based products can be achieved to antibiotic vs antiviral order sumamed 500 mg visa enhance their attractiveness virus respiratorio discount 250mg sumamed amex. The addition of germinated cereal grains to antimicrobial over the counter cheap 500mg sumamed free shipping prepared porridge increases its nutrient density while keeping it suf ficiently liquid to be swallowed by infants (Kohajdova and Karovicova, 2007). The major advantages of fermentation are its low cost and the fact that it is a low tech procedure accessible to poorer rural societies. In African civilizations food fermentation plays a major role in combating food spoilage and foodborne disease (Franz et al. In addition, it enhances the nutritive value, appearance of the food, and reduces the energy required for cooking. Cereals and pseudo-cereals are usually consumed in the form of bread, breakfast cereals, or cereal bars in devel oped countries. In developing countries the consumption of fermented cereals in the form of beverages, cakes, or porridges is common. This kind of food could increase consumption of cereals and pseudo-cereals in developed countries. The manufacturing techniques, microorganisms responsible for the fermentation, raw materials, and processing after fermentation vary worldwide. Nonwheat Cereal-Fermented-Derived Products Chapter 17| 425 There are four main types of fermentation processes: alcoholic, lactic-acid, acetic-acid, and alkali fermentations. The most common fermentation for cere als is lactic-acid fermentation, which contributes to the safety and nutritional quality while achieving different taste and consistency. Alcoholic fermentation is mostly used for production of fermented-cereal alcoholic beverages. Typical fermented nonwheat cereal foods and beverages are traditionally produced from maize, sorghum, millet, rice, etc. The fermentation is mostly carried out sponta neously and involves mixed cultures of yeasts, bacteria, and fungi. Some micro organisms may participate in parallel, while others act sequentially, changing the dominant flora during the fermentation process. The type of bacterial flora developed in the particular food depends on the water activity, pH, salt concen tration, temperature, and composition of the food matrix (Blandino et al. The tropical developing countries have a long history of fermenting various raw materials including cereals. Naturally fermented cereals account for up to 80% of the total energy intake in many African countries and provide an impor tant source of dietary protein (Guyot, 2012; Franz et al. In many regions, different names and raw materials may be used for the preparation of traditional food products. Fermented food products based on rice such as burong isda are typical in the Philippines, idli and dosa are traditionally consumed in India, maize is used to prepare pozol and atole agrio in Mexico and Guatemala, and teff (belonging to the millet family) is used for preparation of injera in Etiopia and Eritrea (Guyot, 2012). For more extensive information about traditional cereal-based fermented food, see Blandino et al. The suitability of selected nonwheat cereals, pseudo-cereals, and legumes for new probiotic food development was recently monitored and it was shown that buckwheat, dark buckwheat, barley, oat, soya, and chickpea inoculated with Lb. In order to meet consumer expectations, great effort is being put toward the design of products, especially staple foods, with improved health-promoting attributes. However, bakery products made from nonwheat cereals usually do not attain the same quality as wheat bakery products, and their production in large quantities is unprofitable (Penas et al. To take advantage of the favorable dietary characteristics of nonwheat cereals while maintaining the quality of traditional wheat bakery products, so-called blended flours based on wheat with limited portions of other cereals may be utilized. Keeping this approach in mind, products fortified with oat, rich in glucan, are considered to be a valuable part of the human diet, considering their outstand ing nutritional and healthy values and relatively standardized bakery quality. Production of sourdough from a special fine whole grain oat flour fraction and potentially probiotic Lb. The rate of staling after 3days of storage was comparable to that of the control sample without the addition of sourdough (Blazekova, 2015).
References:
- https://www.jhsph.edu/research/centers-and-institutes/johns-hopkins-education-and-research-center-for-occupational-safety-and-health/2017MARCOEM/Lavin_MARCOEM2.pdf
- http://www.webcir.org/revistavirtual/articulos/2019/1_marzo/rsna/leukodystrophies.pdf
- https://www.sgasd.org/cms/lib2/PA01001732/Centricity/ModuleInstance/848/Karyotyping%20Activity.pdf
- https://www.ijmrhs.com/medical-research/iron-deficiency-anemia-and-associated-risk-factors-among-teenagers-in-najran-saudi-arabia.pdf
- http://samples.jbpub.com/9780763752828/52827_ch01_souza.pdf