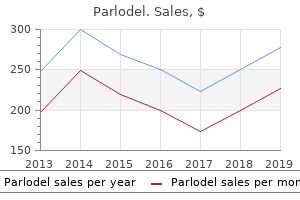
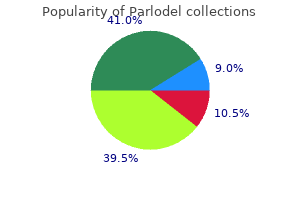
"Order 1.25mg parlodel overnight delivery, mental illness 6 year old."
By: Michael A. Gropper, MD, PhD
- Associate Professor, Department of Anesthesia, Director, Critical Care Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, CA

https://profiles.ucsf.edu/michael.gropper
Reviewer comments: It is concerning that this patient continued to receive ivosidenib after developing such a serious toxicity mental health xanax generic 2.5mg parlodel free shipping. On day 94 pathological mental conditions 1.25mg parlodel overnight delivery, she presented to the hospital with bilateral upper extremity weakness mental health 6 month section discount parlodel 2.5 mg mastercard, including difficulty holding objects and dropping glasses. She was not answering questions and appeared to have seizure activity with bilateral hand twitching and abdominal contractions. She was then noted to have T-wave inversion on telemetry and troponin was elevated to > 14. Later noted to be obtunded with spasticity of the right arm, forearm, and contracture of the right hand. She still had right hand grasp weakness that was improving, but prevented her from feeding herself. Thus, it is possible that the true incidence of mucositis attributable to ivosidenib is much lower than reported. Furthermore, the non-clinical data demonstrated erosions and mucosal inflammation in rats, supporting plausibility (see Section 5. This is consistent with nonclinical data, which demonstrated hepatic toxicity in rats and monkeys (see Section 5. Note that mucositis was seen less commonly in the solid tumor patients, but was still seen in 11 (7%) patients, suggesting that it is a true adverse drug reaction. Renal insufficiency was seen in 2% of solid tumor patients and 1 (1%) healthy volunteer. The non-clinical data supports a possible effect on the kidneys based on medullary tubular vacuolation and tubular necrosis in the renal medulla in rats (see Section 5. In general, adverse events were uncommon on the healthy volunteer studies (n=126. Review of fatigue across dose levels did not reveal a clear dose toxicity relationship (100% at 100 mg bid, 25% at 300 mg daily, 39% at 500 mg daily, 47% at 800 mg daily, and 29% at 1200 mg daily. The median time to onset of the first event of dizziness was 47 days (range 1-393 days. Laboratory Findings For standard clinical laboratory test results, the applicant provided summaries of absolute values over time, and for a subset of the laboratory tests, shifts in toxicity grade from baseline to worst treatment-emergent value. However, it appears that there is no treatment-related adverse impact of ivosidenib on platelet and neutrophil counts. Hemoglobin appeared to take a slight dip in the first cycle, after which time slow, moderate increases were observed. Vital Signs the applicant did not identify any unexpected trends or clinically meaningful post-baseline findings in vital sign parameters. A total of 23 events of hypotension (using grouped preferred term, see Appendix 14. The most frequently reported arrhythmias were tachycardia (n=11), atrial fibrillation (n=8), and sinus tachycardia (n=7. Reviewer comments: the findings of atrial arrhythmia are similar to what would be expected in the underlying patient population. Ventricular arrhythmias included ventricular tachycardia (n=2), ventricular extrasystoles (n=1), and ventricular arrhythmia (n=1. It is difficult to make firm conclusions based on the sample size and the amount of missing data. This may be related to the increased number of prior regimens associated with myelotoxicity in younger subjects. Of these, 2 patients developed benign tumors (lipoma, hemangioma and cholesteatoma) and 4 patients developed skin cancers that are typically resectable (1 basal cell carcinoma, 2 squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and 1 malignant melanoma. The remaining 3 developed endometrial cancer (n=2) and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma (n=1. The spectrum and frequency of second primary malignancies identified on this trial are similar to that of the baseline patient population. Pediatrics and Assessment of Effects on Growth There were no data submitted that addressed short-term or long-term safety in pediatric patients. The subjects were enrolled in the 300 mg daily (n=1), 500 mg daily (n=2), and 1200 mg daily (n=2) groups.
Increased up- Quality criteria and artefacts take can be observed in active epileptogenic Compliance with the above procedures may foci disorders of brain is water discount 2.5 mg parlodel overnight delivery, tumours and infammation mental disorders by symptoms generic parlodel 1.25 mg with amex. Known mor- be expected to ensure an appropriate mental treatment centers oklahoma city 1.25 mg parlodel with mastercard, sym- phological changes such as atrophy should metrical and readily interpretable represen- be considered in the interpretation. Internal landmarks can be used for reorientation to the following list identifes some possible achieve a standardised image display. Reori- sources of misinterpretation that must be entation procedures based on the intercom- taken into consideration when deciding missural line are commonly used. The display whether a scan matches quality criteria: of additional coronal and sagittal images is mandatory. The images should be critically ex- - Insufcient attenuation correction amined by technologists after the scan to en- - Soft tissue or skull uptake following sure that quality criteria are matched. Similar results regarding the associa- to improve accuracy in stereotactic biopsy. Another radiopharmaceu- investigate neuroendocrine tumours such as tical introduced for imaging of cellular pro- phaeochromocytoma and neuroblastoma. Choline is usually the study of primary brain tumours because labelled with 11C or 18F. With regard to the metabolic pathways and tumour features, the main families of avail- able radiopharmaceuticals are summarised in Table 5. High-grade tumours showed an early peak of activity followed by a sharp decline whereas low-grade tumours showed a more smoothed curve with a gradual decline [25]. Owing to the many further evaluations be- yond the early feasibility studies, it is the most commonly used radiopharmaceutical for this purpose in diferent countries. The increased phosphorylcholine synthesis in tumours constitutes the substrate for the Ohtani et al. The concentration of choline in nor- a correlation between 11C-choline and the mal cerebral cortex is low, whereas moder- histological tumour grade, with higher cho- ate uptake is seen in the choroid plexus and line uptake in high-grade gliomas, and sug- cavernous sinus. The authors would like to thank Sabrina Leonardi and all the technologists working in the Nuclear Medicine Department at Humanitas Research Hospital for their pre- cious help. Boellaard R, Hristova I, Ettinger S, Sera T, Stroobants S, sociation of Nuclear Medicine. Prediction of survival in glioma patients by means of positron emission tomography. Diferential expression of sst1, sst2A, primary/recurrent gliomas: initial experience. Consequently it is now possible to assess not the available radiopharmaceuticals include only cerebral blood fow and energy metab- brain perfusion tracers and neurotransmis- olism but also neurotransmission [2]. The length of the centre of rotation, preventing displace- time for which restrictions are imposed var- ment of the head to the periphery of the feld ies depending on the duration of the distur- of view; the canthomeatal line. The restrictions extending from the ear to the eye) should be may include dietary constraints, withholding oriented as vertically as possible; and there of medication and control of environmental should be no rotation or lateral tilt of the variables, such as exposure to visual, auditory head. Special attention processing applications allow reorientation should be paid to potential disturbances in of the data after acquisition; however, these the minutes prior to injection of the radio- data manipulations may introduce errors, in- pharmaceutical and during the uptake phase. In uncoopera- patient, reduce the probability of movement tive patients, sedative medication (e. Table 1) maceutical uptake phase, thereby avoiding can be used according to the clinical indica- sedation-induced blood fow changes [7, 8]. The challenge por- of these variations, images should be com- tion is performed frst and if this yields normal pleted within 4 h after injection owing to the results, omission of the baseline study may be radioactive decay [7]. Patients with focal era bed and allowing closer positioning of the epilepsy refractory to therapy may beneft detectors around the patients head.
Purchase parlodel 2.5 mg visa. Cannabis Use Disorder - causes symptoms diagnosis treatment pathology.
In a hemodynamically stable patient mental health treatment services generic parlodel 2.5mg visa, once the primary survey is determined to be intact mental health symptom checker order 1.25 mg parlodel mastercard, the exam should then proceed to the secondary survey to sufficiently assess the patient from head to toe for external signs of injury mental conditions symptoms purchase parlodel 2.5mg mastercard. Physical examination should include auscultation, visual inspection, manual palpation, and percussion of the chest wall. Depending on the mechanism of injury, particularly blunt trauma, the physical exam may not demonstrate outward signs of injury. Therefore, a chest x-ray is indicated if there is a clinical history of a high-risk mechanism for trauma, or if there is any clinical signs of chest injury present on the child. A surveillance anterio-posterior chest X-ray can be obtained without significant difficulty in a supine, immobilized patient. The x-ray should be examined systematically to evaluate for pleural injury, pulmonary contusions, mediastinal abnormalities, and rib fractures. If findings on chest x-ray are inconclusive for hemothorax or pneumothorax, the study can be supplemented with a bedside ultrasound of the chest. Positive findings for pleural injury or effusion warrants management with chest tube thoracostomy. Other chest x- ray findings for thoracic injury, including rib fractures and pulmonary contusions, should prompt admission for pain control and pulmonary hygiene. If rib fractures present or the patient history is not congruent with the patients presentation, social work involvement may be necessary to assess for possible child abuse. Mediastinal abnormalities on chest x-ray or clinical history of high speed acceleration-deceleration traumas warrant further imaging in a hemodynamically stable patient. Computed tomography angiography should be performed in these select cases to efficiently evaluate for aortic, 325 esophageal, or tracheobronchial tree injury. Aortic injuries require admission to the intensive care unit for strict heart rate and blood pressure control. Esophageal and tracheobronchial tree injuries require further endoscopic examination and immediate surgical intervention. Hemodynamically stable patients, who are asymptomatic, without significant mechanism of injury, and negative radiographic findings of intrathoracic injury may safely be discharged. Otherwise, an injured child should be admitted for cardiopulmonary monitoring, pain management, and radiographic reassessment as indicated. Hemodynamically Unstable Thoracic Trauma In a hemodynamically unstable patient with altered mental status or unresponsiveness, the airway should be secured immediately with endotracheal intubation. Verification of proper tracheal intubation may be established with the appreciation of symmetric bilateral breath sounds and appropriate change in the end-tidal carbon dioxide detector. Fluid resuscitation should be initiated with a 20 mL/kg bolus of isotonic crystalloid fluid such as Lactated Ringers or normal saline. If access is not obtained in 2 attempts or 90 seconds, intraosseous access should be obtained without delay. During resuscitation the mechanism of injury and external signs of thoracic injury should be assessed to determine the etiology of cardiovascular collapse. Life- threatening conditions associated with thoracic injuries include tension pneumothorax, massive hemothorax, cardiac tamponade, and cardiac arrest. A patient that has suffered blunt or penetrating chest injury to the chest presenting with hypotension and unilateral diminished breath sounds should be quickly assessed for tension pneumothorax. The trachea is evaluated for midline position and the internal jugular veins are examined for distention. Tension pneumothorax is a clinical diagnosis and treatment should not be delayed for radiographic imaging. If the constellation of signs and symptoms are present and clinical suspicion is high, needle thoracostomy should be nd performed immediately. Introduction of a large bore angiocatheter in the 2 intercostal space, mid-clavicular line to the affected side will evacuate the pleural space of air and alleviate tension physiology. Chest tube thoracostomy is subsequently performed to definitively address the pneumothorax. If the patient is hemodynamically unstable with unilateral diminished breath sounds and does not clinically appear to be demonstrating tension physiology, hemorrhage into the chest may potentially be the cause of shock. If the patient responds to fluid resuscitation, a prompt chest x-ray should be performed to evaluate for a large hemopneumothorax.
Grade 2 toxicity led to treatment discontinuation in a significant minority of patients disorders of brain 0 brain purchase 1.25 mg parlodel otc. Results: Data from 28 patients and 47 tumors before and after surgery was included mental disorders judgment generic parlodel 1.25 mg with visa. Thus mental illness picture test buy parlodel 1.25 mg on-line, timing of surgery is important and should precede medical treatment with growth inhibitors like bevacizumab. The exact effect of surgery on the extent of hearing preservation and the duration of hearing stability post-surgery is currently evaluated. Its pathophysiology is poorly understood in these conditions but there is probably a role of the inhibitory effect of neurofibromin. Third line treatments include strong opioids (with rigorous monitoring) and botulinum toxin A (for peripheral neuropathic pain in specialist settings. Stimulation techniques are increasingly proposed alone or in combination with pharmacotherapy, because of a generally better side effect profile; they include transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and noninvasive brain neurostimulation techniques particularly repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Invasive techniques such as spinal cord stimulation are proposed for refractory cases. Therapeutic perspectives include the development of compounds acting on new targets and the implementation of an invididualized therapeutic approach. Neuropathic pain often presents with a characteristic set of symptoms and clinical signs distinct from those associated with purely inflammatory pain. Accordingly, the pathophysiological mechanisms and the therapies that have proven most effective at treating these distinct conditions differ from one another. Pain is a common but poorly understood and inadequately treated symptom of peripheral nerve sheath tumors such as those caused by neurofibromatosis and schwannomatosis. In this presentation, I will discuss some of the basic biological mechanisms underlying neuropathic pain and how these mechanisms might relate to pain in peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Methods: We found that inducible conditional disruption of the Smarcb1 gene in Schwann cells does not lead to changes in peripheral nerve morphology or Schwann cell proliferation or cell cycle-related gene expression. However, mice with targeted Smarcb1 disruption in Schwann cells demonstrate increased pain sensitivity. We are testing if the effects of factors derived from Lztr1 mutant Schwann cells are distinct from those of Schwann cells with Smarcb1 mutations to determine if loss of either gene results in distinct mechanisms of pain signaling. A vast variety of resistance mechanisms have been identified and several strategies of combination or sequential treatments are evaluated in order to delay the occurrence of resistance. These targeted agents are now evaluated in earlier disease stages in the adjuvant and neoadjuvant settings with very promising results. They are associated with a large spectrum of adverse events, new to the clinicians, but that are usually tolerable and easy to manage. These have generated hypothesis-driven pre-clinical studies that we are pursuing at the moment. Velez Reyes*1, Nicholas Koes2, Gabriel Kaufmann2, Mariah Berner2, David Largaespada3 1Medical School, 2College of Biological Sciences, 3Medical School, Department of Pediatrics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States Disclosure of Interest: G. The business of all these companies is unrelated to the contents of this abstract. No studies to date provide descriptions of early development, nor rotes to social impairment. Behavioral domains include observer examinations and parent reports of cognitive and adaptive function. These findings highlight the importance of motor functioning delay over social skills for future animal models and early treatment protocols. The next step is assessing whether these delays persist at 14 months, which will be presented and discussed. We will further consider the impact of motor delay on neurocognition, based on quality metrics and head-motion data from our eye-tracking battery. Methods: We mined and integrated available data of reported patient mutations resulting in individual exon or multi-exon deletions with computational predictions of exon skipping effects on the structural and physicochemical features of the mutant protein. Sources for patient information are the Leiden Open Variation Database, Human Gene Mutation Database, and various online publications. This information was combined with available structural data from the Protein Database.
References:
- https://www.iasp-pain.org/files/Content/ContentFolders/GlobalYearAgainstPain2/MusculoskeletalPainFactSheets/ShoulderPain_Final.pdf
- https://www.aafp.org/afp/2015/0315/p365.pdf
- https://www.med.umich.edu/1libr/Gyn/TLH.pdf