"Generic oxybutynin 5mg online, medicine definition."
By: Pierre Kory, MPA, MD
- Associate Professor of Medicine, Fellowship Program Director, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, Mount Sinai Beth Israel Medical Center Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York

https://www.medicine.wisc.edu/people-search/people/staff/5057/Kory_Pierre
Infants <30 days old and children who had received any doses of rotavirus vaccine were excluded treatment kitty colds generic 5 mg oxybutynin mastercard. Data collection Anonymised data were extracted from patients’ medical notes and the computerised data sys tem by a single investigator and entered into a database medicine reviews cheap oxybutynin 5 mg on line. Reporting of dehydration was based on the documentation of the clinician in the notes or the electronic data system symptoms rabies cheap oxybutynin 2.5mg mastercard. Differences between groups were ana lysed using Fisher’s exact test (two-tailed) for categorical variables and the Student t-test or Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables, after checking for normality of distribution using the D’Agostino-Pearson and Shapiro-Wilks tests. The study was conducted in accordance with the Research Governance Framework for Health and Social Care (2005), the World Medi cal Association Declaration of Helsinki (1996), the Data Protection Act (1998) and the current applicable regulatory requirements. Baseline characteristics and clinical presentation Baseline characteristics and clinical presentation are shown in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. Demographics of children with rotavirus-positive and rotavirus-negative gastroenteritis. Presentation and management of children with rotavirus-positive and rotavirus-negative gastroenteritis. Variable Rotavirus Positive Gastroenteritis Rotavirus Negative Gastroenteritis P value N = 50 N = 66 Diarrhoea; n (%) 43 (86%) 62 (95%) 0. Laboratory results of children with rotavirus-positive and rotavirus-negative gastroenteritis. There were no significant differ ences in serum sodium, potassium, glucose, urea, creatinine, alanine aminotransferase, C-reac tive protein, neutrophils or lymphocytes between groups. In almost all the cases with neurological signs (21/22, 95%), gastroenteritis was community-acquired. Other stool pathogens identified in association with seizures were norovirus (n = 4, one of whom had co-infection with adenovirus and one with sapovirus) and astrovirus (n = 1). Discussion In this case-control study, children with rotavirus gastroenteritis more frequently presented with dehydration, metabolic acidosis and fever compared to children with non-rotavirus Table 4. Complications in children with rotavirus-positive and rotavirus-negative gastroenteritis. Afebrile and febrile seizures and transient reduced consciousness were noted in a substantial proportion of children from both groups, but encephalopathy was found only in children with rotavirus gastroenteritis. Dehydration and metabolic acidosis secondary to fluid loss are commonly reported compli cations of gastroenteritis. The findings of this study are consistent with previous studies glob ally reporting that rotavirus causes gastroenteritis that is more severe and of longer duration than gastroenteritis caused by other viral pathogens [11,15–18]. One of the striking findings in the present study was the high frequency of neurological complications in previously healthy children presenting with gastroenteritis. Seizures associated with viral gastroenteritis were first described by Morooka in 1982 [19]. Other viruses, such as adenovirus, sapovirus and norovirus have also been implicated [24]. The term ‘convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)’ has been widely used to describe non-febrile seizures that are associated with gastroenteritis in the absence of clini cal signs of dehydration or electrolyte imbalance [25–28]. A multicentre study of 128 children from Italy found that the onset of convulsions usually occurs within four days after the onset of gastroenteritis. The duration is usually under five minutes (76%), but prolonged convulsions or status epilepticus may occur [27]. The possibility of developing epilepsy is low and the use of long-term treatment with antiepileptic drugs is not recommended [22,27]. Com pared to CwG, febrile seizures develop earlier during the course of the illness and tend to last longer [30,31]. However, despite these minor differences, both febrile seizures and CwG are considered to have a good prognosis [28,32]. Our hypothesis was that children with rotavirus gastroenteritis would have higher fre quency of seizures and neurological complications than children with non-rotavirus gastroen teritis. Although this was not confirmed, there was a trend towards more encephalopathy, with all 3 cases occurring in the rotavirus-positive group and none in the rotavirus-negative group. The underlying mechamisms of neurological manifestations of rotavirus infection are not completely understood.
However medications ending in pam buy 5 mg oxybutynin with mastercard, the 10-year-old girl in the vignette has only had symptoms for 2 years and has associated nystagmus medications restless leg syndrome buy generic oxybutynin 2.5 mg online, so attentional disorder is not a likely diagnosis medications pregnancy buy oxybutynin 2.5mg on line, and a trial of methylphenidate would not be helpful. Ophthalmology referral would be helpful to diagnose nystagmus, but not as helpful as electroencephalography to determine the cause of nystagmus. A psychology referral would be helpful if these episodes were behavioral in origin, but not in making a diagnosis of seizure. The patient has a history of pre–B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia diagnosed 7 years ago, which was treated with chemotherapy for 3 years. He subsequently developed graft versus host disease and was on a tapering course of prednisone over the last 2 months. He was most recently taking 5 mg orally once daily until his prednisone was discontinued 1 week ago. This is seen in conditions such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia, Addison disease, or other conditions leading to primary disease. The resulting decreased adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion leads to isolated glucocorticoid deficiency, which causes retention of free water and subsequent hyponatremia. Because the renin-angiotensin system is not affected, potassium concentrations are generally normal. However, if the adrenal glands have atrophied from prolonged suppression from exogenous steroid use, then it is possible to have abnormalities in both sodium and potassium. She is being treated twice daily with a combined high dose inhaled corticosteroid and long acting β-agonist, and once daily with a leukotriene receptor antagonist. She demonstrates chronic rhinitis for which she is treated daily with a nasal steroid and a nonsedating antihistamine. Despite her treatment and reported excellent adherence, the patient has an asthma control test score of 17. She continues to require short acting β-agonist administration 3 to 4 times per week for exercise intolerance, cough, or wheezing, and has required 3 courses of systemic steroids in the last 4 months during weather changes or viral illnesses. Prior radioallergosorbent tests for cat, dog, peanut, and egg allergies were negative. The lungs are well aerated, but you note a prolongation of the expiratory phase of respiration with a scattered end expiratory wheeze. The parents inquire about the utility of skin testing for allergies in their child. In the optimal care of an asthmatic patient, asthma-related control is assessed at each visit to the health care provider. When poor control in the asthmatic patient is encountered, assessments should be made regarding adherence to therapies; additional attention should be given to the potential for comorbid conditions such as allergic rhinitis. The patient in the vignette demonstrates chronic rhinitis and family members exhibit symptoms that are consistent with atopy. Furthermore, there are multiple potential or proven aero-allergens in the home, including pets and exposure to cigarette smoke. The prevalence of asthma and allergic rhinitis have increased in parallel in recent decades. As many as 60% of asthmatic individuals experience rhinitis and there is a corresponding 20% prevalence of asthma in patients with allergic rhinitis. The complexity found in the overlapping clinical spectra of asthma and allergic rhinitis is exacerbated by the fact that asthma is not a single disease, but rather a variable and multifactorial disease process that may be modified by genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. The spectrum of atopic disease is similarly complex and different “endotypes” of atopic disease exist that are unique with regard to their association with asthma. Furthermore, both serum specific (immunoglobulin E [IgE]) and skin allergy tests are prone to variability in interpretation. Therefore, it has been recommended that both skin testing and specific IgE testing be quantified rather than simply reported as positive or negative. The presence of sensitization to aero-allergens is a recognized risk factor for the development of asthma. In children younger than 3 years of age with recurrent wheezing, evidence of sensitization to 1 or more aero-allergens is considered one of the major criteria that predicts wheezing at school age (asthma predictive index).
Oxybutynin 5 mg fast delivery. If You Are A Vietnam Veteran You Are Engaged In The VA Claims Process (Whether You Know It Or Not!!).
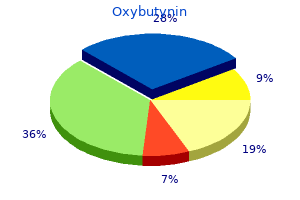
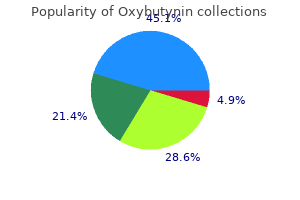
Mulhathi (Licorice). Oxybutynin.
- Dosing considerations for Licorice.
- How does Licorice work?
- Upset stomach (dyspepsia), when a combination of licorice and several other herbs is used.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Licorice?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96849
In the normal fetus between the 11th and 14 early 12th week of gestation treatment room oxybutynin 5 mg on-line, the nasal bone may appear poorly ossified or absent treatment 4 ulcer quality oxybutynin 5 mg. Ductus Venosus the ductus venosus is an important vessel in the fetus as it directs highly oxygenated blood from the umbilical vein medicine advertisements cheap 2.5 mg oxybutynin, through the foramen ovale and into the systemic arterial circulation. Abnormalities in the Doppler waveforms of the ductus venosus in the first trimester have been reported in association with fetal 13 aneuploidies, cardiac defects, and other adverse pregnancy outcomes. Ductus venosus waveforms can be assessed qualitatively by observing the A-wave component of the Doppler spectrum, which reflects the atrial kick portion of diastole. An alternative approach relies on the quantification of the ductus venosus 14 waveforms by using indices such as the pulsatility index for veins as a continuous variable. We do not recommend routine assessment of ductus venosus flow in all pregnancies, but rather in pregnancies at increased risk for congenital heart disease or in pregnancies with an intermediate risk 14 for aneuploidy. This approach decreases the subjectivity of the measurement and increases its accuracy. This is defined by the presence of the echogenic tip of the nose and rectangular shape of the palate anteriorly, the translucent diencephalon in the center, and the nuchal membrane posteriorly. More than one measurement must be taken and the maximum one that meets all the above criteria should be recorded in the database. Note the presence of two other echogenic lines, superior to the nasal bone, representing the nasal skin (short arrow) and the tip of the nose (long arrow). The magnification of the image should be such that the fetal head and thorax occupy the whole screen. Minor deviations from the exact midline plane would cause non-visualization of the tip of the nose and visibility of the zygomatic process of the maxilla. Tricuspid Regurgitation Color and pulsed Doppler of the tricuspid valve can be obtained in the apical four-chamber view of the fetal heart by placing the color Doppler box and the pulsed Doppler sample volume over the valve at the level of the annulus (Fig. Tricuspid regurgitation in the first trimester is a common finding in fetuses with aneuploidies (trisomies 21, 18, and 13) and in those with major congenital 14 heart malformations. Trivial tricuspid regurgitation, defined by the presence of a small regurgitant jet at the valve annulus, is a common finding in the first trimester and has been reported in the 21 majority of normal fetuses. Similar to the ductus venosus, we do not recommend routine assessment of the tricuspid valve for tricuspid regurgitation in all pregnancies, but rather in pregnancies at increased risk for congenital heart disease or in pregnancies with an 14 intermediate risk for aneuploidy. There are two types of ultrasound examinations in obstetrics—screening or routine examinations that are offered to all pregnant women irrespective of risk and targeted examinations that are indication driven and offered to pregnant women with increased risk. The second trimester morphology ultrasound examination has become a screening examination in most countries and is offered routinely to all pregnant women. The fetal echocardiogram, on the other hand, is a targeted ultrasound examination that is offered to pregnant women at increased risk for congenital heart disease. The first trimester ultrasound examination is 22 now considered a screening examination in many countries but is still indication driven in others. As more data accumulate on the value of the first trimester ultrasound in the assessment of fetal malformations, and more expertise develops in the performance of the examination, the authors believe that the first trimester ultrasound examination will be routinely offered to all pregnant women where local resources allow. The role of the first trimester ultrasound is evolving from pregnancy dating and aneuploidy screening to the first look at fetal anatomy to detect major malformations. Guidelines for the performance of the first trimester ultrasound were published recently. Note that the insonation angle is almost parallel to the direction of blood flow in the ductus venosus (arrow). Criteria for optimal display of ductus venosus Doppler waveforms are shown in Table 1. A represents the atrial contraction phase of the cardiac cycle in the Doppler waveform. The examination should be undertaken during fetal quiescence the magnification of the image should be such that the fetal head and thorax occupy the whole screen. The filter should be set at a low frequency (50–70 Hz) so that the A-wave is not obscured. The sweep speed should be high (2–3 cm/s) so that the waveforms are spread allowing better assessment of the A-wave. Note that the sample volume is placed over the valve to cover inflow and regurgitation when present. In this example, there is no tricuspid regurgitation in systole (double arrow) and the Doppler spectrum is normal with E corresponding to early diastole and A corresponding to the atrial kick portion of diastole. The magnification of the image should be such that the fetal thorax occupies most of the image.
Effective migraine treatment begins with the early recognition that an attack is pending followed by immediate treatment medicine keeper oxybutynin 2.5mg low cost. Migraine sufferers are encouraged to medications given during labor buy oxybutynin 5 mg on-line take an active role in managing their headaches by avoiding common triggers medications may be administered in which of the following ways 2.5mg oxybutynin visa, making lifestyle changes, and taking their medication at the first sign of migraine pain. Patients taking certain migraine and antidepressant medications together may be at risk for a dangerous chemical imbalance. Migraine drugs include almotriptan (Axert), fi fi fi naratriptan (Amerge), sumatriptan (Imitrex), and zolmitriptan (Zomig). Serotonin is a brain hormone that keeps our mood stable and our appetite in check, as well as serving other functions. When two or more drugs that affect serotonin levels are taken together, it can increase the amount of serotonin and may lead to bothersome or dangerous symptoms. This is called “serotonin syndrome” in which high levels of the chemical serotonin build up in the brain and cause toxicity. This can often lead to a person taking multiple and possibly mechanism-overlapping medications. The questions to discuss with a health care professional are: Are the medications actually making a difference? In other words, taking pain medications is a choice that each person must make by weighing the benefits vs. When the risks appear to outweigh the benefits of taking a pain medication, reducing the dose and ultimately discontinuing the medication should be considered. This is called weaning or tapering particularly when the individual has become dependent on the medication. The term “detoxification” is sometimes used interchangeably but should be limited to cases with opioid addiction. The goal of tapering/weaning down the dose is to safely discontinue medications that do not seem helpful in reducing pain while allowing the body to adjust while monitoring for negative effects of withdrawal symptoms. Oftentimes, people discover they feel better taking lower doses, fewer medications, or not taking medications at all. It is best to check with the health care professional before altering the medication regimen by taking less of the medication or stopping it. It is dangerous to abruptly stop taking some medications (sometimes referred to as going “cold turkey”). Because the body develops physical dependence to some medications when they are taken regularly, abrupt withdrawal or too rapid a reduction in the dose of these medications can be very uncomfortable or even hazardous to one’s health. It depends on the type of medication, how much, and for how long the medication has been taken. A sound approach is to talk to a health care professional before making any medication changes or if you have any other questions or concerns. Answer the following questions about each medication, and the person with pain should write down the answers beside the name of each medication during the visit: o For what condition is this medication being prescribed? The health care professional determines the rate at which the dose is reduced, and adjustments can be made as necessary. For example, reasonable opioid weaning protocols suggest decreasing pill intake by 10 20 percent per week, as tolerated. Hydration (drinking water), relaxation, and emotional support are all important to enhance the likelihood of success. Sometimes weaning or discontinuing medication (especially opioids) is most safely accomplished under the close supervision of a specialist (such as a pain or addiction medicine specialist) in a medically-supervised program to prevent complications and severe withdrawal symptoms. Other drugs to manage withdrawal symptoms during detoxification o naltrexone (Vivitrol) – an extended release non-addictive, once-monthly injection to prevent relapse in opioid dependent patients when used with counseling following detoxification. Alcohol has no place in the treatment of chronic pain, although some individuals turn to alcohol forrelief of their pain. It is important to discuss the use of alcohol with your health care provider, including the amount, frequency, and type of alcohol consumed.
References:
- https://www.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/lse/literature/ELISA%20Disease%20Detection%20Modeling.pdf
- https://www.stamfordhealth.org/app/files/public/2935/mso_education-manual_update.pdf
- http://millenniumassessment.org/documents/document.317.aspx.pdf
- http://www.baytallaah.com/bookspdf/61.pdf